Introduction: The Overlooked Legacy of Display Interfaces

Many discussions of monitor cables are focused on the standard suspects: HDMI, DisplayPort, USB-C–but few are aware of how earlier standards like those of the DB9 connector affected modern display technology. The shift from serial-based video signaling to the current digital interfaces that are high-speed wasn’t just a leap forward, the process was one of incremental improvements that were rooted in the history of computing and industry.
This article will look at:
- The intriguing role of DB9 connectors in the early display systems
- How the principles of serial communication from the past created modern monitor cables
- What are the reasons that some industries still depend on hybrid setups today?
1. The DB9 Connector’s Unexpected Role in Early Video Systems
Before VGA was adopted as the standard in the 1980s, various display systems that were proprietary used Serial communication–often via DB9 ports–to send video signals. Even though we are now able to are able to connect DB9 to RS-232 (a serial interface that is used for peripherals and modems) but early workstations for engineering and industrial monitors also employed modified DB9 configurations to allow videos with low resolution.
Why This Matters Today
- Certain older industrial monitors utilize the DB9-based control signals in conjunction with the latest video signals.
- Understanding the older systems will help to determine compatibility issues in retro computers or hardware that is specialized.
To get a deeper understanding of the technical basis of DB9, check out this full overview of DB9 connectors
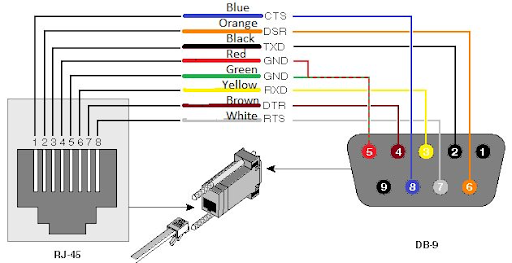
2. How Serial Signaling Indirectly Shaped Modern Monitor Cables
Early digital displays had to face an important challenge: the balance between bandwidth and efficiency of the pin. The pin count of DB9 was limited, which made it necessary for engineers to come up with multiplexing methods, which were later developed to create DVI as well as DisplayPort

Key Evolutionary Steps
- VGA (1987): Borrowed the rugged shell of DB9 but added an analog RGB signaling.
- DVI (1999): Introduced TMDS (Transition Minimized Differential Signaling) A high-speed serial technique that is reminiscent of the robustness of RS-232.
- DisplayPort (2006): Completely adopted information transmission via packets, an evolution away from the serial protocols.
This progression is why the latest Monitor cables are geared towards shielded differential pairs, a direct response to the noise issues first addressed in the DB9 era.
For a thorough analysis of the latest choices, check out this guide on various types of monitor cable.
3. Hybrid Systems: Where DB9 and Modern Cables Coexist
In medical imaging, aviation and factories, it’s not uncommon to see ports for DB9 that work with DisplayPort as well as HDMI. Why?
Three Practical Reasons
- Control Signals: DB9 often handles the configuration of devices, while video cables handle the display.
- Legacy Hardware: The replacement of equipment worth millions of dollars is not possible Adapters fill in the gaps.
- Noise immunity The serial protocols surpass USB to control long distances in environments with a lot of EMI.
Conclusion: A Nod to the Past in Cutting-Edge Displays
The switch from DB9 to the modern monitoring cables was not a complete change; it was a cumulative accumulation of lessons learned from serial communications. Modern high-bandwidth interfaces owe nebulous dues to the limitations of the older connectors.
For historians and technicians alike Understanding this lineage provides the depth of troubleshooting and system design. Learn the complete story of DB9 connectors or look at today’s top cables for monitoring to discover how much we’ve progressed.





